I will explain the outline of the economic trend index, the Bank of Japan Tankan, the price index, money stock, monetary base, etc., which are typical economic indicators. Each feature and source of presentation is essential knowledge.
Economic Trends Index
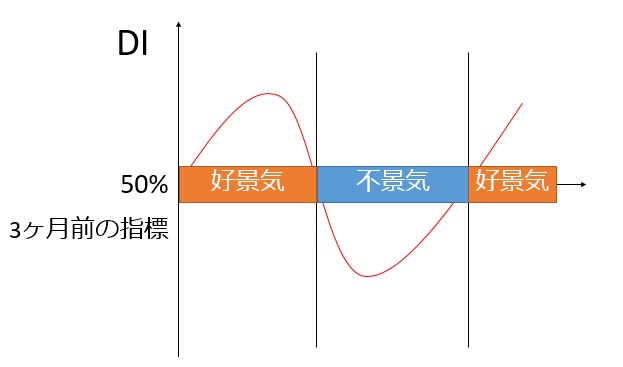
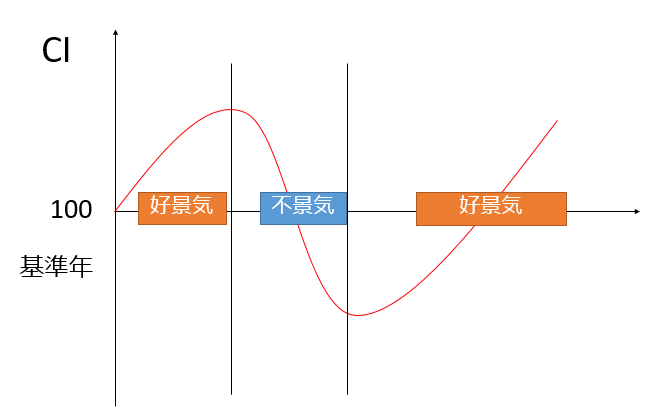
There are two economic trend indices: the Composite Index (CI) and the Diffusion Index (DI), which are published monthly by the Cabinet Office. Simply put, CI measures the magnitude of economic fluctuations, and DI measures the direction of economic fluctuations.
Based on data from three months ago of 28 economic indicators susceptible to economic activity, DI is expected to be 100% if all economic indices expand and 0% if all economic indices deteriorate, and if it is more than 50%, it is judged to be a booming economy and a recession if it is less than 50%.
CI can use the index of a year as 100 to see how much the current situation has changed from there.
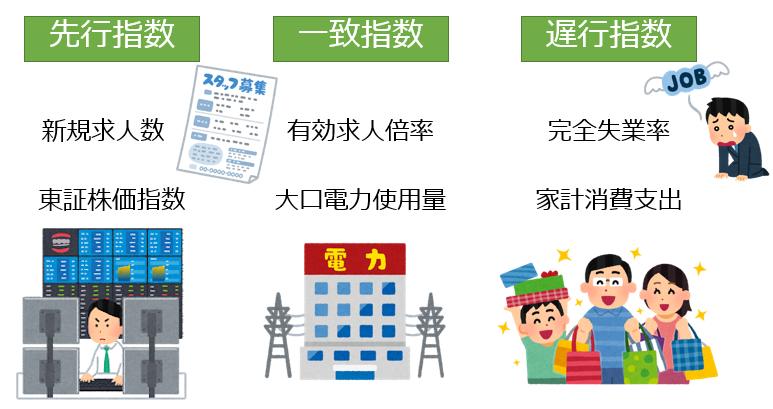
There are three main types of economic indices used to calculate DI and CI: leading, matching, and late indices.
- Leading Index: Moving Ahead of the Economy
- Match Index: Nearly in line with the economy
- Slow Index: Slow To The Economy
Bank of Japan Tankan
The Bank of Japan Tankan is also known as the National Short-Term Economic Survey of Enterprises. This is a questionnaire survey on economic trends for managers of 10,000 companies nationwide, and isannounced four times a year by the Bank of Japan. A typical indicator is the “Business Conditions DI,” which is based on the ratio of companies that say the economy is good and the ratio of companies that say it is bad.

Price Index
Corporate Goods Price Index (CGPI)
It is a chronological view of price fluctuations in products in business-to-business transactions, and is announced monthly by the Bank of Japan. The service price is not included.
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
It is a time series of price fluctuations in goods and services purchased by households nationwide, and is announced monthly by the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications.
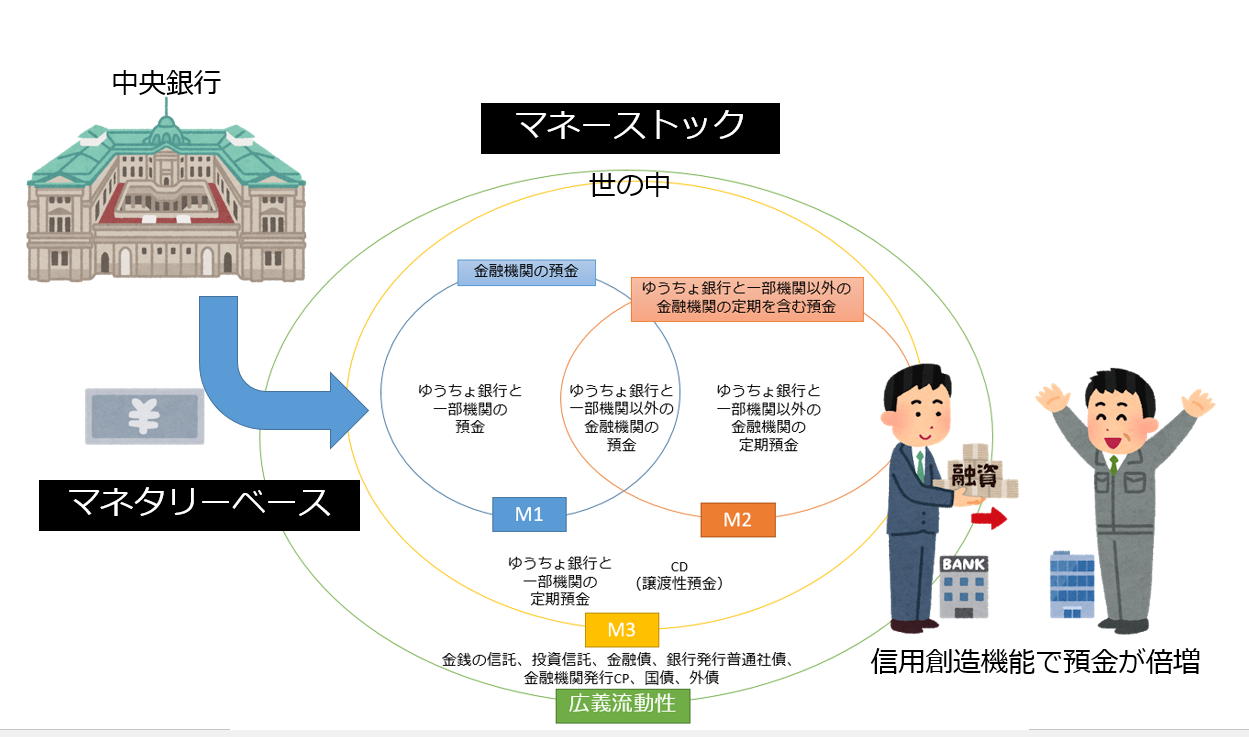
Money Stock
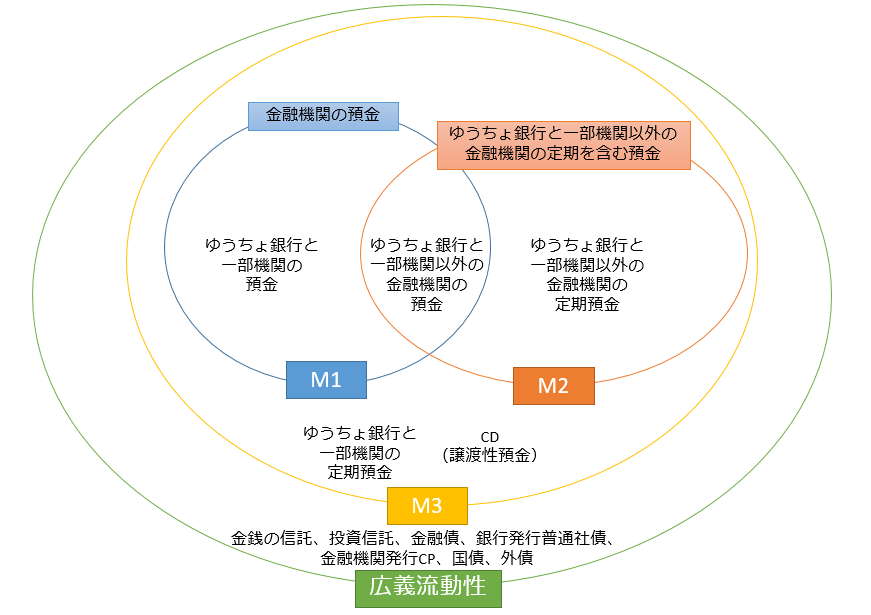
The balance of the amount of currency held by individuals, corporations, and local governments, excluding financial institutions and central governments, is called money stock. It is also called money supply. The total amount of currency supplied by the financial sector to the economy as a whole, and in a word, it means the total amount of money in the world.
The range of financial institutions and currencies here varies from country to country, and in Japan, M1, M2, M3, and broad liquidity are defined.
Monetary base
The sum of the cash currency and the currency deposited by private financial institutions in the central bank (in the case of Japan, the Bank of Japan) is called the monetary base. Simply put, it means the total amount of currency supplied by the central bank.
At first time, the total amount of currency supplied by the central bank (monetary base) looks like the total amount of money (money stock) in the world, but in reality, due to the credit creation function of financial institutions, money stock is several times the monetary base.