I will explain what an investment trust is, what structure it is, and what kind of classification it is. This is a field that has a lot of technical applications, but it is remembered by images by easy-to-remember illustrations.
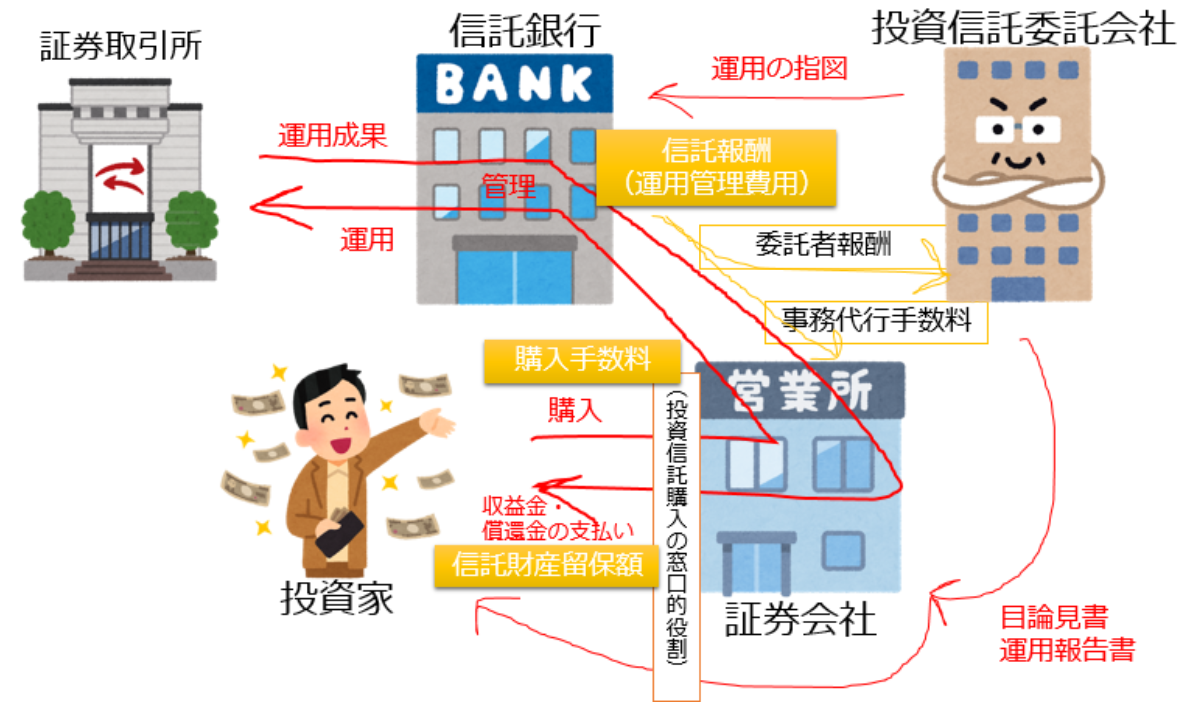
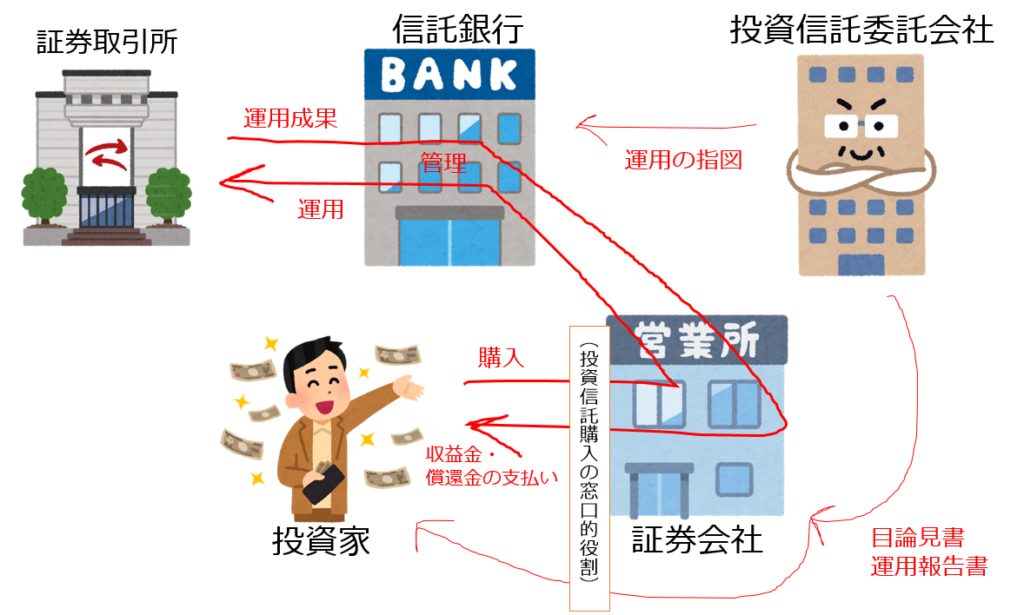
Structure of Investment Trust
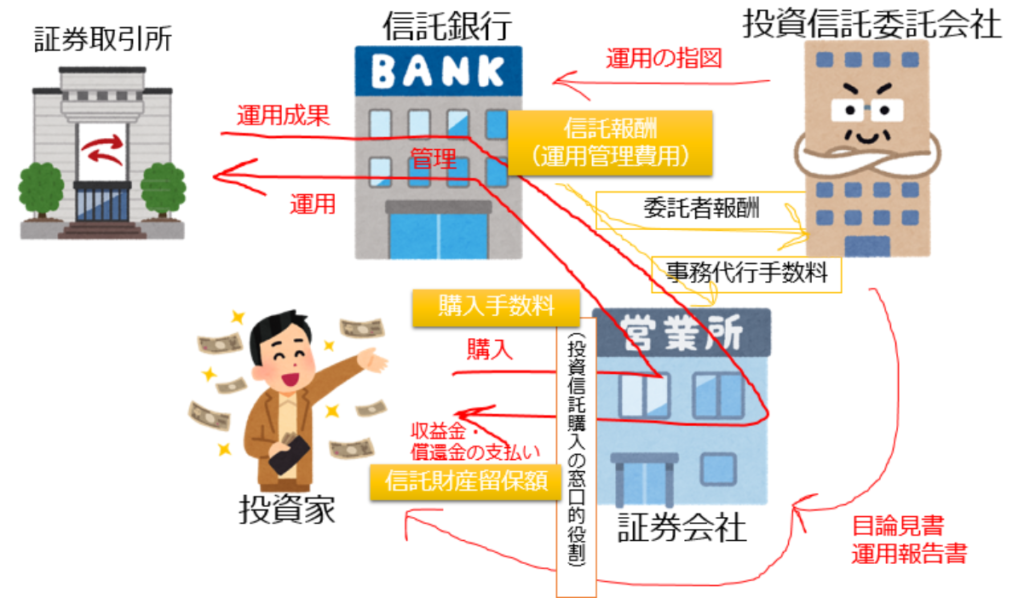
There are four characters related to investment trust:
- Investors (beneficiaries): Individuals and corporations that buy investment trust
- Sales companies (securities companies,etc.): Companies that recruit and sell investment trust, and deliver prospectus and management reports.
- Investment trust subcontractors (contractors): Companies that give trustees operational instructions and make prospectus and management reports.
- Trust banks (trustees): Banks that store and manage trust assets and operate in accordance with the orders of the trustee.
Classification of Investment Trusts
There are various classifications of investment trust depending on the point of focus.
Classification by the difference of the operation target
Investment trusts are financial instruments that are distributed investments in various subjects such as stocks and bonds, but are classified into the following two types, especially depending on whether they are incorporated into investments for stocks.
- Stock Investment Trusts: Investment trusts that canbe used to stocks
- Public and Corporate Bond Investment Trusts: Investment trusts that cannot be Included in stocks at all
In a stock investment trust, it doesn’t matter whether you actually put it in just because you can put stocks in.
The reason why stocks are attracting attention here is that stocks are more at risk of price fluctuations for public and corporate bonds. This classification allows you to roughly determine the safety of mutual funds.
Originally, investment trusts are highly secure financial products because they are distributed investments, but since public and corporate bond investment trusts are operated only by highly secure public and corporate bonds, they are even more secure.
Classifications depending on the method of purchase
- Unit investment trusts: Investment trusts that can only be purchased during the initial recruitment period
- Additionalinvestment trusts: Investment trusts that can be purchased and exchanged at any time atthe market price
Classification by differences in the structure of investment trusts
- Contract-type investment trusts: A general investment trust, as shown in the figure above, that is a trust agreement between a investment trust subcontractor and a trust bank.
- Corporate investment trusts: Since an investment corporation is established and investors become investors, investment trusts such as stocks.
Classification by differences in operating methods1
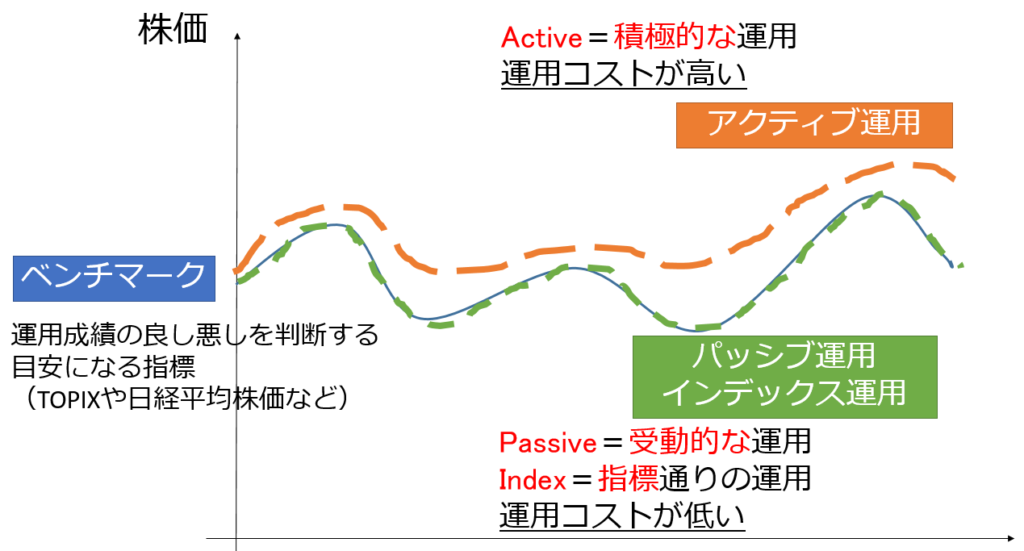
- Active operation:A method to achieve operating results that exceed the target index (benchmark)
- Passive (index) operation: a method that aims to operate in conjunction with the targetindicator (benchmark)
Intuitively, investors should choose active operations with better operational performance, but active operations are expensive to investigate and high operating costs. Therefore, since the burden increases for investors in the form of commissions for buying and selling and holding, active operation is not always better.
Classification by differences in operating methods2
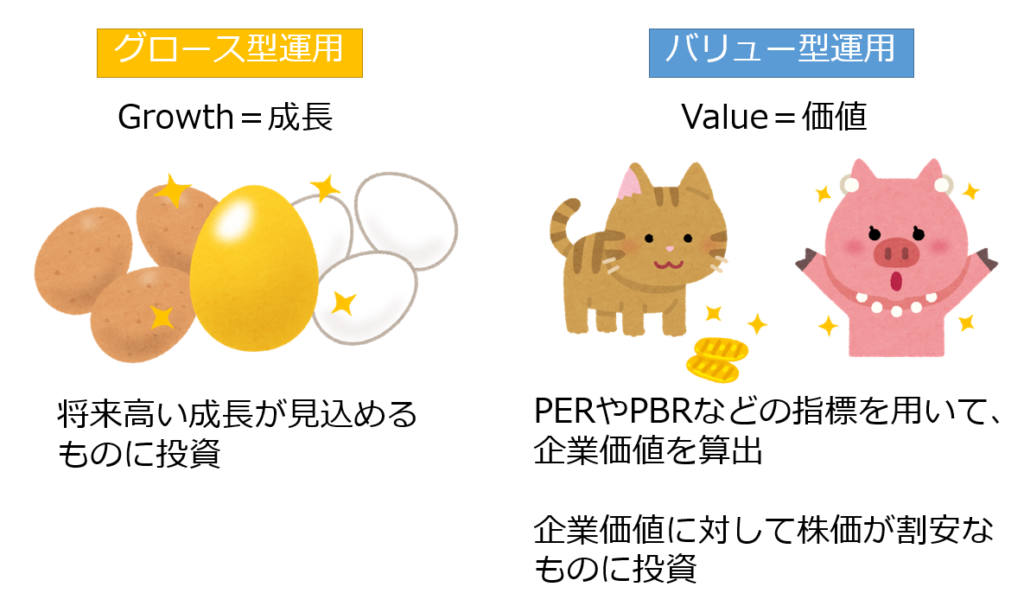
- Value-based operations: How to invest in companies thy stock prices are likely to be undervalued
- Growth-based operations: How to invest in companies that are expected to grow at a high rate of growth
Cost of purchase, holding, and cancellation of investment trusts
There is a cost for each investor to purchase, hold, or cancel an investment trust.
- Purchase fee (application fee): Fees in which investment trusts are purchased
- Trust remuneration (management and management costs): Fees in which investment trusts are held
- Retained trust assets: Fees in which investment trusts are cancelled
From among the trust fees, the trust company is paid the contractor’s fee, or the sales company is paid an administrative agency fee.
When choosing an investment trust, you need to pay attention not only to your performance, but also to the percentage of commissions that are taken.