I will explain the Financial Instruments Sales Law, the Financial Instruments and Exchange Act, the Consumer Contract Act, and the Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds, which are the acts related to the transaction of financial instruments, in a diagram that is easy to remember.
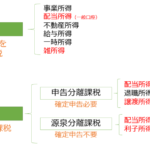
Financial Instruments Sales Law
Financial Instruments Sales Law is one of laws that stipulates that a seller of a financial instrument is responsible for damages in the case of a loss by failing to explain to the customer the important matters to be explained to the customer. Important matters to be explained include the possibility of a crack in the main account, factors, and details of the contract.
This offers a wide range of financial products, including deposits, trusts, insurance, securities, and derivatives.

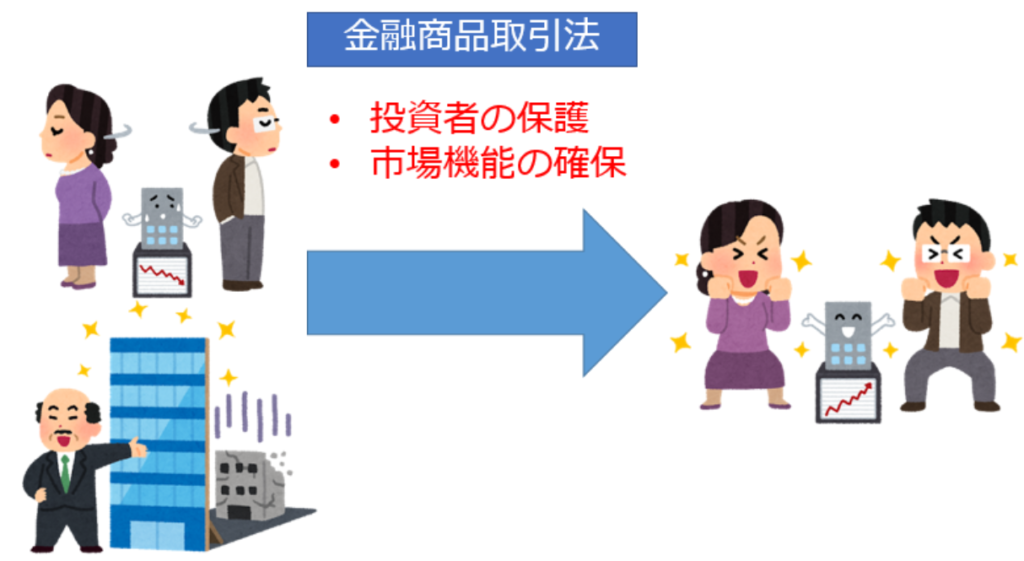
Financial Instruments and Exchange Act
The Financial Instruments and Exchange Act is a law aimed at cross-sectional legislation to protect investors, securing market functions for “savings to investment” and responding to internationalization of financial and capital markets.
Simply put, it is designed to clarify the order of financial transactions and create an environment that is accessible to everyone.
The Financial Instruments and Exchange Act strengthens various regulations over a wide range of transactions and organizes the entire financial transaction. Specifically, it has the following contents.
- To clarify the classification of the financial instruments business, the trader must apply to the Prime Minister and register it.
- Regulations on behavior, such as false notices of financial instruments businesses and prohibition of theproviding of assertive judgments
- We classify investors as specific investors (professionals) and general investors (amateurs), and the latter includes advertising regulations, obligations to deliver documents prior to conclusion of contracts, and principles of conformity.
- Required to publish financial statements of securities and submit confirmations on a quarterly basis by listed companies
Domestic futures transactions are not subject to regulation.
Consumer Contracts Act
The Consumer Contract Act is a law that allows a contractor to cancel an application or acceptance of a contract in the case of a contractor’s misididation by the act of a business operator in all contracts between an individual consumer and a business operator.
Here are some specific examples of unfair solicitations that allow cancellation of contracts:
- Falsehood notice: If you have an explanation that is different from the facts
- Excessive volume sales: When a business operator contracts knowing that there is an excessive amount
- Non-announcement of Disadvantageous Facts

In the sale of financial instruments, if it violates the provisions of both the Financial Instruments Sales Act and the Consumer Contract Act, both laws apply.
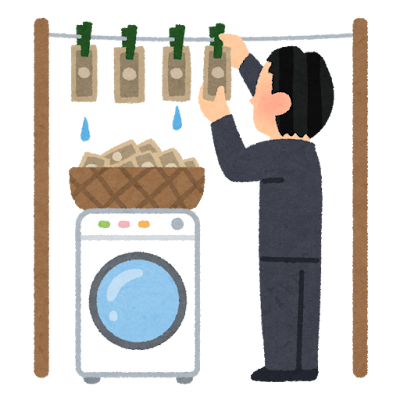
Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds
The Act on Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds is a law aimed at preventing money laundering and terrorist funding, and stipulates identity verification when conducting transactions.

Businesses subject to laws and regulations include not only financial institutions, but also jewelry and precious metal handling companies, telephone receptionists, and lawyers.
Here are some specific examples of transactions that require financial institutions to verify their identities:
- When you open an account
- When you make a transaction involving the payment of cash in more than 2 million yen
- Transfer in cash exceeding 100,000 yen
- When you make a loan transaction
When performing the above transactions, the financial institution must confirm the customer’s “specific matters (name, address, date of birth)” and “purpose of transaction” and “occupation”. When you do business through an agent, you must confirm the confirmation of the person of both the customer and the agent.